professionals need to have the correct knowledge. There is a lot of misinformation about autism. Can contact Altogether Autism.
What is Autism?
It is a life long condition - no cure
Children are born with autism - signs seen at 3 years
Is not a disease, rather its important to use strategies to support living.
Autistic people are Neurodiverse - they experience the world in a different way and need strategies to live in a Neurotypical world.
Autism can be positive or negative in the way we look at it. The word disorder is negative (ASD). Autistic people prefer to use autism.
Maori/indigenous worldview of autism:
- Takiwaaitanga - a more positive term - in my own time and space.
Support needs in the following:
Autism isn't defined as high or low functioning anymore. On a spectrum.
Levels are used now for practicality. 3 the highest level of support.
Girls diagnosed later than boys as they imitate and mask.
Autism characteristics:
Autism and strengths:
Focus on strengths - a more positive picture of self.
Provides a better understanding of who they are.
Characteristics can be looked at negatively or positively.
How an autistic brain works:
We can miss things if we haven't found a way to communicate.
Executive functioning:
Different parts of our brain talk to each other so we can organise, plan, remember, deal with change etc. Working memory can be affected.
Challenges
Becoming anxious, take a breath, slow down, can not regulate
Strategies:
Thinking about the cognitive level of the child is really important in deciding which strategy is more effective.
Important to engage in listening not just hearing but holistically.
To promote self-regulation physical activity can help.
Autism and Anxiety:
Life doesn't work to their strengths, expectations of other people, life is very anxious. Sometimes a refusal to do a task is showing anxiety. It can be seen as difficult. When anxious we lose our skills.
Look at the person closely and try to understand what is happening.
When they are relaxed, look for times and spaces to teach them about things they may be active about.
Strategies for anxiety:
Use pictures to communicate needs (PECS).
Limiting choices is really important - 2 choices
Be mindful of task avoidance.
smell the flower/blow out the candle - use pictures to support
The disconnected brain:
Emotions are controlled by the brain. When connected it works well.
An autistic brain is not connected, emotions take over.
Meltdown or Tantrums:
A meltdown is not a tantrum. A meltdown is a medical event, rather than behaviour event. There is no control over the reactions they are showing. A tantrum can lead to a meltdown ( a seizure attack). Make sure they are safe, take others away.
3 stages of meltdown:
Build up:
Capture the meltdown early, help the child cope with the stress then eliminate the meltdown.
After the meltdown has happened there is a recovery stage. The key to this stage is recovery. Relax, Reconnect, reflect, (with the other children in the class too), recharge, re-prepare.
Behaviour:
Reframing the behaviour.
Behaviour is a way of communication. No behaviour that happens for no reason, always a reason, maybe communicating I cant do this, this is too much, avoid/need.
Reframe your view from won't to can't. Find the why, the reason. Is there a stressor that prevents the child from doing, is there a need, is there a skill deficit.
Sensory Sensitivity
Autistic children have sensory sensitivities. Senses processed by central nervous system, our brain processes these. My brain tells me what this is, and how to respond. Proprioception - our body space, where we are, in space.
Behaviours we may see because of senses:
Interoception is another sense. It is understanding what is happening inside your body. How is your body feeling? Autistic people struggle with this a lot. They experience feeling but don't know what the feeling is. Eg eating - don't know when to stop. When in a situation of anxiety they don't know what to do.
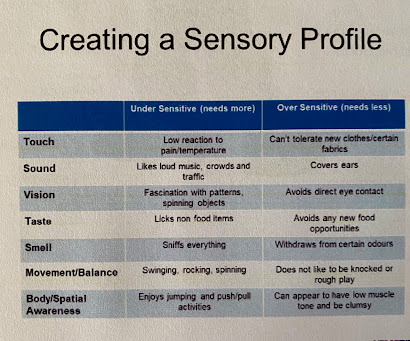
Sensory profile:
Stimming:
Anything repetitive - behaviour or action. It can be done to self soothe, calm down, enjoy the stimulation, distract, habit, regulate ourselves. Stimming serves a purpose. Is it a concern for the child? or stigmatisation for us.
Communication:
This is one of the main support areas for autistic people. There are lots of differences in communication. Non verbal doesn't mean I have nothing to say, you have to listen closely. Frustration occurs and they can't communicate their needs. problem behaviours are used to communicate.
Visual supports
The child can complete more tasks by themselves and become independent having used visual supports.
Break it down to the steps.
First Then.
First, you read then you go outside.
keep motivated.
Social Stories
teach about a situation, a skill, a transition
Positive sentences, keep it simple.
Visual schedule
What is going to happen throughout the day.
Take the card off that they have done. Indicates time to move to the next step.
Video modelling:
Use to teach a skill or how transitions work.
Video doesn't change, so a great tool to use. Also visual rather than spoken.

























Comments
Post a Comment